Release notes for the Genode OS Framework 24.08
Genode 24.08 puts emphasis on the tracking of the supported 3rd-party software and consolidation work. It features the Qt6 application framework in addition to the time-tested Qt5, consistently updates all Linux-based components and PC device drivers from Linux version 6.1 to version 6.6.47, and updates Mesa to version 24.0.8. The consolidation work revisits the framework's base and GUI interfaces with respect to C++20 style, the move away from exception-based error handling, and the use of strict types.
Combining Genode's recent advances of on-target debugging with the Goa SDK, the release introduces remote debugging via Goa (Section Debugging). Further topics of version 24.08 range from enhanced board support for i.MX-based devices (Section Improvements for NXP's i.MX family), over the exploration of AVX on x86 (Section NOVA microhypervisor), to steady improvements of Genode's custom microkernel (Section Execution on bare hardware (base-hw)).
Base framework and OS-level infrastructure
Reduced reliance on the C++ exception mechanism
In version 21.11, we introduced the Attempt utility as an alternative to exception-based error handling. While gradually applying this pattern, in particular for newly introduced interfaces, we observed our code becoming more rigid and concrete, leaving no condition unconsidered. Given this added assurance, we ultimately decided to remove the reliance on C++ exceptions from the base framework over time. The current release takes a huge leap in this direction.
- base/id_space.h
-
A new Id_space::apply overload takes a second functor missing_fn as argument, which is called whenever the lookup fails. It thereby allows the use of the Id_space utility without Unknown_id exceptions.
- util/xml_node.h
-
The two Xml_node::attribute accessors have been removed along with the Nonexistent_attribute exception. Attributes are generally accessed via the attribute_value method, which handles the case via a default value.
- Core RPC interfaces
-
Exceptions have been entirely removed from the RPC interfaces provided by the core component, namely Trace, Pd, Cpu, Rm, and Region_map.
While touching these interfaces, we took the opportunity for modernization and consolidation of both the interfaces and their implementations. E.g., core's trace service received a welcome facelift, e.g., the former use of basic types got replaced by dedicated types.
The revised Region_map interface uses an Attr compound struct for specifying arguments to the attach operation, which makes the intent of client code more obvious. The operation returns a Range instead of a Local_addr now. The Region_map::State type got renamed to Fault.
- base/child.h
-
The Child_policy::Nonexistent_id_space exception has been removed by making the server_id_space mandatory for each policy. The former Child::Process and Child::Process::Loaded_executable classes got replaced by class functions that return failure conditions as return values, eliminating the use of C++ exceptions by the child framework.
The overall ambition of cutting back the use of C++ exceptions is not limited to the base framework but can be observed for critical components as well. In particular, the NIC router received a profound rework in this respect.
Cultivation of C++20 programming style
One year ago, we enabled C++20 as default. With the current release, we took the chance to update the codebase according to this version of the standard.
- C++20 function template syntax
-
The auto keyword can be used in many places where template arguments had to be declared manually. We updated all sources of the base framework accordingly.
- Using using instead of typedef
-
C-style type aliases are no longer used within the framework.
- util/geometry.h
-
The header has been moved from the os repository to the base repository. Point, Area, and Rect have been turned into plain compound types, making x, y, w, h, at, and area accessible without a method call. Rect is now represented as a tuple of Point and Area, which is the most common form of initialization. The companion utilities have been updated (constexpr, eliminating out parameters) as well.
- util/color.h
-
The Color type has been converted from a class to a POD type by replacing the constructors by the named create functions rgb, clamped_rgb, and clamped_rgba. This enables the initialization of color values using the { .r = ... } syntax and makes the type usable in const expressions. The change also narrows the type for the color components and alpha values to uint8_t. So possible integer overflows of computed values are detected by -Wconversion.
Tightened GUI-session interface
On our road map, we anticipated intensive work on user-facing topics, many being related to graphical user interfaces. While approaching these topics, we sensed that the clean implementation of our ideas would benefit from a revisit of the framework's existing GUI infrastructure, in particular the GUI-session interface as provided by the nitpicker GUI server and the window manager. Note that we barely touched this corner of the framework in the past ten years since version 14.08. The changes are as follows.
-
The Gui::Session::session_control RPC function got removed because its functionality has long been superseded by the window manager and layouter.
-
The interfaces and components received a thorough coding-style update, embracing C++20, avoiding plain pointers, using Attr structs for passing attributes, removing the notion of invalid handles/IDs, replacing basic types by dedicated types, and removing the use of C++ exceptions.
-
The out-of-RAM and out-of-caps conditions are now consistently handled by the Gui::Connection, which does no longer inherit the Gui::Session interface and can thereby introduce tailored result types.
-
The creation of top-level views and child views are now two distinct operations (view and child_view).
-
The access of the subsumed framebuffer and input interfaces is now mediated by the plain public members Connection::framebuffer and input. This simplifies the client-side code. E.g., _gui.input()->pending() becomes _gui.input.pending().
-
Corner cases of view-stacking operations are now expressed as dedicated commands. The new stacking commands are FRONT, BACK, FRONT_OF, and BEHIND_OF.
-
View handles are managed as Id_space and hence named view IDs now. The allocation of view IDs has been moved from the server side to the client, which gives clients more flexibility and reduces the surface of possible error conditions between client and server. To ease the client-side ID management, the Gui::Connection hosts a view_ids ID space for optional use. E.g., the new Top_level_view class uses this ID space for ID allocation. This class accommodates the most typical use case of opening a single window.
-
The creation of new views accepts initial view attributes now, which accommodate typical client use cases with less code.
As a note of caution, this line of work will continue over the course of the next release cycle. The GUI-related APIs of the framework are expected to undergo further changes during that time.
Fostered consistency of naming
Within our code base, we are ardent about consistency. However, two relics from the infancy of the project remained standing out like sore thumbs. First, the _drv suffix of driver executables remained at odds with our established style of naming things without artificial abbreviations. Second, the plural naming of the <repo>/src/drivers/ directory nagged us by being inconsistent with the sibling directories test/, app/, server/. The current release rectifies both inconsistencies. The _drv suffix has been dropped and the directory has been renamed to driver/.
Device drivers
Linux device-driver environment (DDE)
We last adapted Linux DDE for kernel 6.1 in May/August 2023. According to our plan of approximately one update per year, it was time to roll up our sleeves for the adaption to Linux 6.6 LTS and ready our driver base for future (especially PC) platforms. With this release, we limited our efforts to the emulation library itself as well as virt_linux and pc_linux driver ports.
Thus, from now on, PC platforms use Linux driver sources of kernel version 6.6.47 for USB host controllers and devices, Wifi and Ethernet adapters, Intel display, lxip TCP/IP protocols, and wireguard. Non-x86 platforms were updated for USB devices and network protocols only, but will be adapted in future releases step-by-step. All drivers work as drop-in-replacements of older versions with respect to integration and configuration.
Our Wifi driver port got amended by an online quality update concerning the currently established connection, which can be enabled by the configuration attribute update_quality_interval. With this feature, user interfaces are enabled to reflect connection-quality changes almost instantly. Additionally, we added support for Intel AX200/9560 wireless adapters and restored support for Wifi devices found in Thinkpad T430 notebooks.
During this release cycle, we analyzed a noticeable network throughput drop resp. CPU load increase when using the PC Ethernet driver. We eventually traced the effect to runtime overhead originating from our DDE memory allocator. The positive impact of a simple allocation-cache implementation confirmed our suspicion veritable. Hence, we replaced our custom allocator by the Linux kernel-internal SLUB allocator that is based on page/folio allocation. The folio API is well hidden in the kernel internals, still in flux, and offers only incomplete (resp. outdated) documentation, which required quite a bit of research efforts reading and understanding the kernel's implementation.
In the end, we improved our emulation implementation sufficiently and managed to get the PC NIC driver to work robustly with gigabit performance and with CPU load reduced by 25-40% on Intel Kaby/Tiger Lake notebooks.
Platform driver
During ACPI suspend, the PCI bridges in the system may forget their PCI configuration. Hence on resume, this configuration needs to be restored to render all PCI devices behind the bridge usable again. With this release, we added support to the pci_decode component to report all relevant information, which is then picked up by the platform driver after an ACPI resume to re-configure the used PCI bridges. This change enables the successful restart of the Wifi driver after resume on many platforms.
Improvements for NXP's i.MX family
The current release comprises a lot of updates and additional support for the i.MX family of devices.
First of all, we have updated all existent Linux driver ports to Linux kernel version 6.1.20. In detail, drivers for the Freescale Ethernet Device (FEC) for ARMv7 and ARMv8, the display management for the i.MX 8M Quad EVK and the MNT Reform 2, as well as the SD-card Host Controller for the same two boards got refreshed.
Alice Domage of Gapfruit AG contributed outstanding work to enable platform support for the i.MX 8M Plus SoC and Compulab's IOT Gateway, which is based on it. Besides clock, powering, and reset support by a platform driver specific to this SoC, support is now available for both Ethernet cards (FEC and ST Microelectronics' STMMAC), SD-card host controller, I2C, and GPIO.
Genode's custom kernel supports two more boards now, namely the F&S Embedded armStone Starterkit and MNT Pocket Reform. Both are using the i.MX 8M Plus SoC mentioned above. The support is currently limited to the very basics, and no peripherals apart from CPU and timer are integrated yet.
For the fine-grained control of GPIO pins, release 21.11, introduced the pin I/O session interfaces, superseding the older Gpio session interface. So far, however, our driver for the GPIO controller as present on all i.MX SoC's merely supported the old interface. With this release, we introduce a pin driver implementing the favored pin I/O session interface instead. All occurrences in packages and run-scripts under Genode's umbrella use the new driver now, which can be found under src/driver/pin/imx within the genode-imx repository. The old driver and the Gpio session interface are still existent. But now, as there is no hard dependency or necessity for it anymore, we mark the old driver as well as the Gpio session interface as deprecated.
Finally, we moved all remaining i.MX specific parts out of Genode's main repository into the genode-imx repository to be consistent with our recent approach of vendor-specific external repositories.
Libraries and applications
Qt6 application framework
With this release, we started updating the Qt application framework from Qt5 to Qt6 by adding an initial port of Qt 6.6.2, covering the qtbase, qtdeclarative, qtshadertools, and qtsvg modules. We are planning to support the qtwebengine module as well in the near future, which will remove the dependency from Python 2 and provide us with a more recent Chromium engine for the Falkon and Morph web browsers.
We also improved the Qt build process for both Qt6 and Qt5 by making sure that Qt libraries are only built when needed and stub libraries generated from symbol files are used otherwise.
The Qt6 port uses updated host tools, which need to be built with the tool/tool_chain_qt6 script. Please note that Qt6 requires CMake version 3.19 or higher to build successfully.
Mesa version 24.0.8
With release 24.05, we updated Mesa to major version 24. During the past few months, we improved the memory allocation and synchronization for Intel's Iris driver and as a side effect updated Mesa to version 24.0.8.
Platforms
Execution on bare hardware (base-hw)
Under the hood of Genode's custom kernel, the way how CPU-local memory is arranged changed fundamentally. The kernel's virtual memory layout now comprises a CPU area. Each CPU has its own slot within this area, containing kernel stack, CPU object data resp. all CPU-local data. This change is transparent to most Genode developers. It was motivated to ease CPU detection and bootstrapping at run time, for kernel stack overflow detection, and for increasing the kernel's flexibility regarding multi-core hardware.
NOVA microhypervisor
The kernel received support to handle the x86 CPU FPU extension AVX, which is a family of SIMD instruction extensions used for optimized implementations of mathematical algorithms, e.g., it is used in multimedia applications. In principle, the kernel has to detect the available AVX versions, e.g., AVX, AVX-2, AVX-512. Depending on the version, it has to save and restore additional FPU state during thread switching. Besides the general availability to Genode applications, the Seoul VMM has become the first user of the feature. The VMM now announces the AVX feature to the guest VMs, so that the guest kernel can enable it and guest user applications can utilize it, e.g., for web browser and video encoding/decoding use-cases. The feature got tested with the Seoul VMM on Intel and AMD systems.
Additionally, we adapted the core component to support Intel SoCs with E-Core only CPUs, which were formerly named Intel Atom and are nowadays branded as Intel N-Series CPUs.
Finally, the NOVA kernel now supports the freeing of vCPU related data structures during VM destruction, got optimized to reduce resource overhead during cross CPU IPC and improved VM MSR exit handling.
Build system and tools
Improved reproducibility
The demand for reproducible builds has been increasing during the past few years. The main hindrance that makes builds unreproducible are timestamps. On Genode, especially components that produce TAR files suffered from this limitation, since the date of the archived data was set to the time of archiving. To avoid this issue, we introduced a customizable global TAR_OPT in Genode's build system that sets the date of the archived files to the date of the epoch and the user/group to one. As a starting point, we added the TAR_OPT to the Qt-build process while other targets will incrementally follow.
Additionally, we enabled our Rump-kernel port to be reproducible.
Goa SDK
Debugging
After the addition of on-target debugging on Sculpt OS in Genode 24.05, it was about time to equip Goa with debugging support as well. For this purpose, the tool received an optional --debug command-line switch, which instructs Goa to consider dbg archives in its download, export and publish steps.
When provided with this switch on goa run, the tool also creates a <project-name>.gdb file in the project's var/ directory. This file contains initialization commands for the GNU debugger (GDB) and can be passed to GDB via the --command argument.
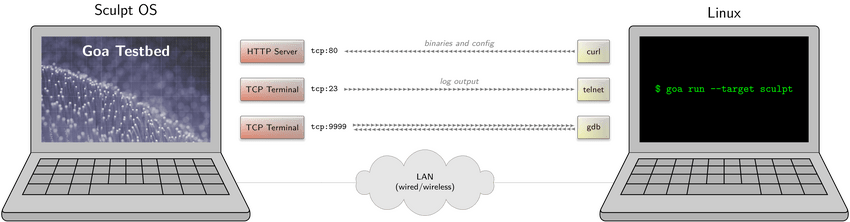
|
The Goa testbed package and preset have been updated accordingly to make use of our debug monitor. The figure illustrates how Goa interoperates with the Goa testbed. Sculpt's default NIC router configuration now comprises an additional gdb domain that is intended to accommodate a single client to which the router forwards port 9999 of the uplink domain. This is intended for making the testbed's debug monitor available as a remote GDB target. Note that these changes will become effective with the next Sculpt release in October. In the meantime, you may cherry-pick the corresponding commit.
Along with debugging support, Goa also received a --with-backtrace switch and a backtrace command. The former instructs the tool to preserve frame-pointer information by supplying the -fno-omit-frame-pointer flag to GCC. The goa backtrace command is a shortcut for goa run --debug --with-backtrace that additionally passes the log output to our backtrace tool.
For detailed instructions, please refer to the corresponding Genodians article.
Meson build system
Projects like Qemu, glib, and Mesa have switched to the Python-based Meson build system. Mesa, for example, produces a large number of generated C/C++ files using Meson features. In order to ease future porting effort of Meson-based projects to Genode, we have added basic support for this build system to Goa.
A Meson project can be built and executed like any other Goa-supported build system with the addition that there can be a meson_args file (analogously to cmake_args for CMake) where additional arguments can be passed to the meson command. Otherwise, Goa will look for a meson.build file in the src directory, which identifies the project's build system as Meson.
As a simple test, you can check out the hello_meson example in the examples directory of Goa.
At the current stage, only binary targets for the x86_64 architecture are supported by Goa/Meson. Shared libraries and ARM support will be addressed next.
Rust & Cargo
From Rust 1.77 onward, the binary distribution of the std library (x86_64-unknown-freebsd) assumes that the underlying OS kernel supports thread-local storage via the FS segment register on x86. As Genode does not provide a TLS area via FS, TLS accesses by the library would end up in invalid memory, which renders the binary version of the std library unusable on Genode. In response, we have implemented a custom Genode target profile for Rust, which allows us to still leverage the FreeBSD port of Rust's standard library while using the emulated TLS model. In order to compile the parts of the std library used by an application for the custom profile, we have moved to using a nightly Rust tool chain. For detailed instructions for setting up the tool chain, head over to the blog post at Genodians.org.
